- index.html
- style.css
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>The flow direction of the main axis and margins</title>
<link href="course.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="world">
<div class="spot">
<div class="skate skate-1 racoon-green"></div>
<div class="skate skate-2 racoon-brown"></div>
<div class="skate skate-3 racoon-orange"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS
.spot {
display: flex;
align-items: stretch;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.skate {
margin: 10px;
min-width: 50px;
min-height: 50px;
}
.skate-2 {
margin-top: auto;
}
.skate-3 {
align-self: flex-end;
margin-bottom: auto;
}
You’ve gone to a different page
Goalscompleted
0
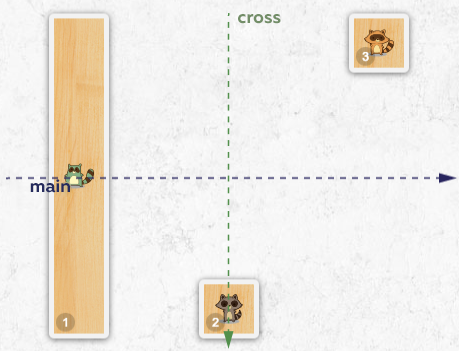
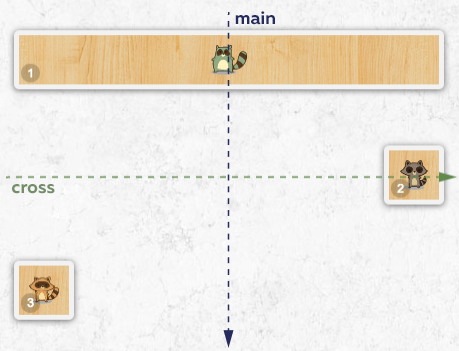
- Change the direction of the main axis to
columnfor.spot. - Then delete the
margin-topproperty from the second skateboard and add themargin-left: auto;property. - Delete the
margin-bottomproperty from the third skateboard and add themargin-right: auto;property.
Comments